API stands for application program interface. A programmer writing an
application program can make a request to the Operating System using
API (using graphical user interface or command interface). It is a set
of routines, protocols and tools for building software and applications.
It may be any type of system like a web-based system, operating-system
or a database System.
Java Compiler: It is a predefined program that converts the high level user written code language to low level computer- understandable byte code language during the compile time
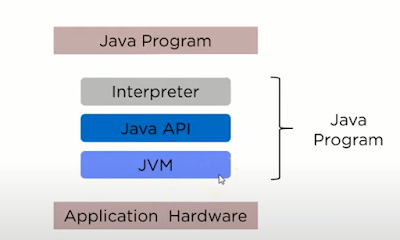
JVM(Java Virtual Machine):processes the byte code obtained from the compiler and generates an output in user-readable format.
Java API:These are integral software packages that come along with JDK.The primary intention of API is to establish communication between applications.
Example:
iostream API are used to interact with Files
jdbc API are used to interact with DataBase
javadoc - Generates HTML pages of API documentation from Java source files.
//Program
/* API MESSAGE DISPLAY */
public class Api
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("This line belongs to API");
}
}
public class Api
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("This line belongs to API");
}
}
ubuntu@ubuntu:~/Desktop/rkjava/api$ javac Api.java
ubuntu@ubuntu:~/Desktop/rkjava/api$ ls
Api.class Api.java
Api.class Api.java
ubuntu@ubuntu:~/Desktop/rkjava/api$ javadoc Api.java







No comments:
Post a Comment